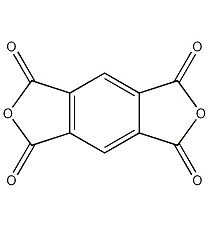
Structural formula
| Business number | 020M |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H2O6 |
| Molecular weight | 218.12 |
| label |
1,2,4,5-Benzenetetracarboxylic dianhydride, Pyromellitic anhydride, 1,2,4,5-pyromellitic dianhydride, Pyromellitic dianhydride, Pyromellitic anhydride, 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride, 1,2,4,5-pyromellitic dianhydride, pyromellitic dianhydride, Hardener, solid lubricants, plasticizer, Cross-linking agent for polyester resin |
Numbering system
CAS number:89-32-7
MDL number:MFCD00005005
EINECS number:201-898-9
RTECS number:DB9300000
BRN number:213583
PubChem number:24865800
Physical property data
1. Properties: White needle-like crystals or powder. Can sublime
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.680
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.69
4 . Melting point (ºC): 289
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 380~400
6. Boiling point (ºC, 3.9997kPa): 305~310
7. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3295.8
8. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -925.1
9. Specific rotation (º): Not available Determined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Not determined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit ( %, V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in dimethyl at room temperature Formamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide,γ-butyrolactone, N-methylpyrrolidone, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, methyl isobutyl ketone, ethyl acetate, insoluble in chloroform, ether, n-hexane, and benzene. It hydrolyzes into pyromellitic acid when exposed to moist air.
Toxicological data
Toxicity classification Poisoning.
Acute toxicity Oral – rat LD50: 2250 mg/kg; Oral – mouse LD50: 2400 mg/kg.
Irritates the skin and mucous membranes and can cause allergies, allergic reactions and other disorders.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 45.11
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 115.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 360.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 94.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 17.88
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 6
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 86.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 16
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 349
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Hydrolyzes to pyromellitic acid when exposed to moist air. poisonous! Operators should wear work clothes, protective glasses and gloves.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place away from light. Keep away from fire, heat sources, sun protection and moisture-proof. Double-layer packaging, with plastic film as the inner layer and cardboard barrels as the outer layer.
Synthesis method
There are many ways to prepare it. The raw materials used can be xylene, trimethylbenzene, tetramethylbenzene or anthracene. Oxidation methods include liquid phase method and gas phase method. 1. Vapor-phase oxidation of tetramethylbenzene is characterized by its simple process, which can eliminate the dehydration to anhydride process. It does not require other oxidants (such as nitric acid, permanganic acid, chromic acid, etc.) except air, and does not require the catalyst required for the liquid phase. Separation process, continuous production, easy to realize automated operation, is the main method of foreign development. 
The raw materials used can also be from 1,2 Starting from 4-trimethylbenzene, it is alkylated with propylene in the presence of a catalyst to generate 1,2,4-trimethyl-5-propylbenzene, and then catalytically oxidized with gas phase air to obtain pyromellitic dianhydride.

2. By xylene (p- Xylene or m-xylene) is obtained by chloromethylation, oxidation and cyclization. The industrial product pyromellitic dianhydride is white to light yellow-green crystal. The melting point of the first-grade product is 284-287°C, and the melting point of the second-grade product is 283.5-287°C. When produced from 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene by the oxidation method, each ton of product consumes 3000kg of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene and 1200kg of propylene.






3. Carbon monoxide method: High purity is obtained by reacting trimethylene and carbon monoxide The intermediate aromatic aldehyde 2,4,5-trimethylbenzaldehyde is then oxidized to obtain pyromellitic acid, and finally dehydrated to generate PM-DA. This method adopts a new carbonylation process with few side reactions, high product purity, high yield, strong selectivity, low corrosion to equipment, and meets environmental protection requirements. It also uses a set of equipment to switch between the production of trimellitic anhydride and PMDA. , lower production costs.
Purpose
1. This product is used as a curing agent for epoxy resin. It has excellent anti-leakage properties for epoxy resin used as casting and laminated motor materials. This product is also used as matting curing agent in the production of powder coatings, polyimide resin and film, high temperature resistant electrical insulating paint, solid lubricant, plasticizer and cross-linking agent of polyester resin, etc. 2.Used as a curing agent for epoxy resin, the reference dosage is 56 parts by mass, and the curing condition is 180℃/15min. Due to its high melting point, it is difficult to mix with epoxy resin. It can be dissolved in phthalic anhydride or maleic anhydride, and is often used as a curing agent when mixed with these anhydrides. The cured product has excellent heat resistance and physical and mechanical properties, and the deformation temperature can reach 200~250℃. It is also used in the manufacture of polyimide, polyimide, polyester resin, plasticizers, surfactants, water-soluble alkyd resins, phthalocyanine blue dyes and fungicides, etc. It is also used as solid lubricant, urea-formaldehyde resin stabilizer, corrosion inhibitor, radiation protection agent and electronic photography toner.
Phthalic anhydride or maleic anhydride is often mixed with these acid anhydrides and used as a curing agent. The cured product has excellent heat resistance and physical and mechanical properties, and the deformation temperature can reach 200~250℃. It is also used in the manufacture of polyimide, polyimide, polyester resin, plasticizers, surfactants, water-soluble alkyd resins, phthalocyanine blue dyes and fungicides, etc. It is also used as solid lubricant, urea-formaldehyde resin stabilizer, corrosion inhibitor, radiation protection agent and electronic photography toner.



